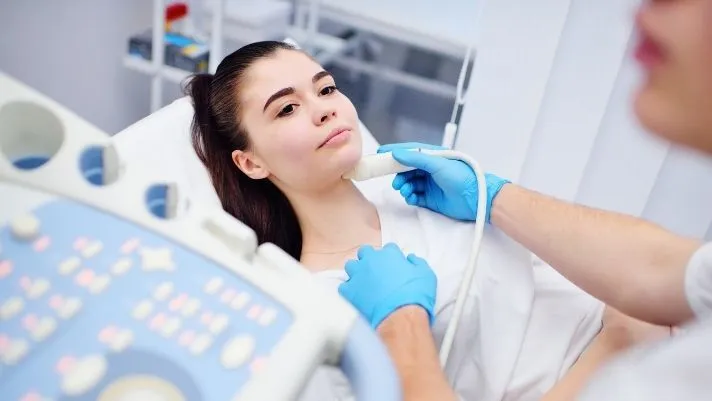
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in endocrinology. It helps doctors see inside the body without surgery. Techniques like MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds can spot issues in the glands. For example, an MRI Colorado search can detect abnormalities in the thyroid or adrenal glands. These images guide treatment and improve care. Knowing how these tools work can make a big difference in managing endocrine disorders.
Table of Contents
What is Diagnostic Imaging?
Diagnostic imaging involves using various techniques to create images of the inside of the body. These images help identify and monitor health conditions. In the field of endocrinology, these images reveal problems in hormone-producing glands.
Common Imaging Techniques in Endocrinology
Three common imaging techniques prove vital in endocrinology:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images. It’s useful in examining the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
- CT Scans (Computed Tomography): Combines X-rays and computer technology to produce cross-sectional images. It helps to evaluate the adrenal glands and detect tumors.
- Ultrasound: Employs sound waves to produce images. It’s often used for thyroid gland evaluations.
Why Imaging is Important in Endocrinology
Beyond just spotting gland issues, imaging assists in:
- Early Detection: Finds issues before they become severe.
- Accurate Diagnoses: Ensures proper treatment by pinpointing conditions.
- Monitoring Progress: Tracks changes and effectiveness of treatments over time.
Comparison of Imaging Techniques
| Technique | Best For | Advantages | Limitations |
| MRI | Soft tissues, brain glands | No radiation, detailed images | Costly, not suitable for all patients |
| CT Scan | Bone, soft tissues | Quick, detailed cross-sections | Radiation exposure |
| Ultrasound | Thyroid, soft tissues | No radiation, portable | Less detailed than MRI or CT |
Case Study: Thyroid Disorders
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a key role in metabolism. Imaging is essential for diagnosing conditions like hyperthyroidism and thyroid nodules. Ultrasound often serves as the first step, providing a clear picture of the gland’s shape and texture. If more details are needed, MRI or CT scans may offer additional insights.
Guidelines and Recommendations
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, early detection of thyroid conditions can prevent complications. Regular imaging, as recommended by a healthcare provider, ensures any issues are caught early.
Conclusion
Diagnostic imaging supports endocrinologists in providing effective care. By using MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds, they gain a clear understanding of gland-related issues. This clarity leads to better treatment plans and improved outcomes. As technology advances, imaging techniques will continue to evolve, offering even greater details and benefits for managing endocrine disorders.